Denise Moussa
Denise Moussa, M. Sc.
I am a PhD candidate in the multimedia security group since February 2021. My research focus is on audio forensics, image forensics and deep learning.
Recent projects
EnvId: A Metric Learning Approach for Forensic Few-Shot Identification of Unseen Environments (Accepted at IEEE TIFS 2025)
Audio recordings may provide important evidence in criminal investigations. One such case is the forensic association of a recorded audio to its recording location. For example, a voice message may be the only investigative cue to narrow down the candidate sites for a crime. Up to now, several works provide supervised classification tools for closed-set recording environment identification under relatively clean recording conditions. However, in forensic investigations, the candidate locations are case-specific. Thus, supervised learning techniques are not applicable without retraining a classifier on a sufficient amount of training samples for each case and respective candidate set. In addition, a forensic tool has to deal with audio material from uncontrolled sources with variable properties and quality. In this work, we therefore attempt a major step towards practical forensic application scenarios. We propose a representation learning framework called EnvId, short for environment identification. EnvId avoids case-specific retraining by modeling the task as a few-shot classification problem. We demonstrate that EnvId can handle forensically challenging material. It provides good quality predictions even under unseen signal degradations, out-of-distribution reverberation characteristics or recording position mismatches.
Now ForReal: Towards Practical Forensic Room Identification with Real-World Audio Data (IEEE WIFS 2024)
Recovering the place of origin of, e.g., a phone call can aid the reconstruction of events in a criminal case. For audio forensics, identifying the recording location exclusively from an audio signal still poses a challenge. While various works address this task, they evaluate on semi-synthetic reverberant speech data in a supervised setting. Thus, there barely exist any empirical insights on practical forensic recording environment identification, i.e., the handling of real-world audio data from case-dependent locations that are unknown to a tool in advance.
In this work, we take a first step towards such a practical scenario. We collect a set of real-world speech from several rooms under varying recording parameters. In forensic cases, audio evidence usually stems from uncontrolled sources, such that factors like the recording position, speaker or microphone can be unknown and reverberation characteristics are of mixed quality. The influence of such factors for room identification is analysed in detail, with several results.
For example, we find that prior knowledge about the recording position strongly aids classification, and that characteristics of a speaker’s voice notably impact performance.
Unmasking Neural Codecs: Forensic Identification of AI-compressed Speech (Interspeech 2024)
Compression traces are an important forensic cue to uncover the processing history and integrity of audio evidence. With continuous advances in the AI domain, efficient generative lossy neural codecs like Lyra-V2, EnCodec or Improved RVQGAN can compete with traditional speech and audio codecs. Their fundamentally different learning based approach compared to analytical lossy compression methods poses a new challenge for audio forensics. This calls for a closer examination of such techniques to prepare forensics for audio evidence processed by AI-based codecs. In this work, we thus want to take a first step towards robustly detecting traces of neural codecs in audio samples. We report that distinctive frequency artefacts enable for identifying neurally compressed audio and fingerprint specific AI-based codecs. We further analyse the robustness towards cross-dataset testing and noise, downsampling, and traditional compression post-processing.
Point to the Hidden: Exposing Speech Audio Splicing via Signal Pointer Nets (Interspeech 2023)
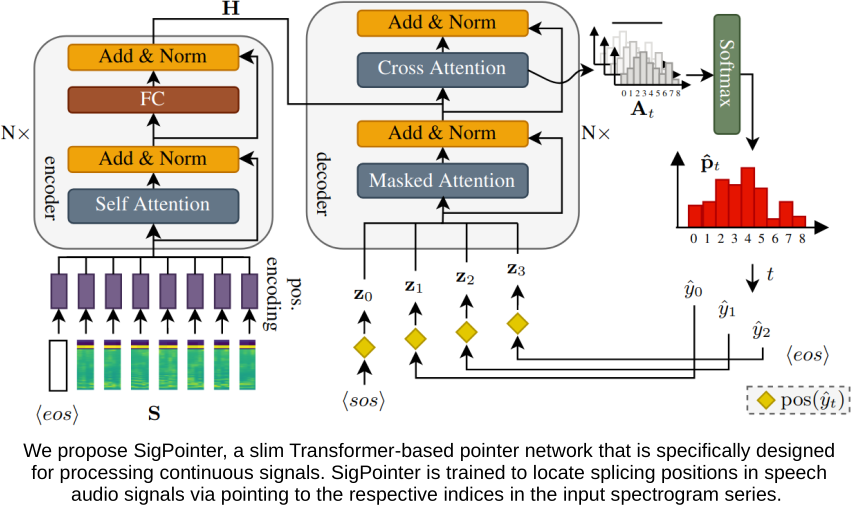
Verifying the integrity of voice recording evidence for criminal investigations is an integral part of an audio forensic analyst’s work. Here, one focus is on detecting deletion or insertion operations, so called audio splicing. While this is a rather easy approach to alter spoken statements, careful editing can yield quite convincing results. For difficult cases or big amounts of data, automated tools can support in detecting potential editing locations. To this end, several analytical and deep learning methods have been proposed by now. Still, few address unconstrained splicing scenarios as expected in practice. With SigPointer, we propose a pointer network framework for continuous input that uncovers splice locations naturally and more efficiently than existing works. Extensive experiments on forensically challenging data like strongly compressed and noisy signals quantify the benefit of the pointer mechanism with performance increases between about 6 to 10 percentage points.
Forensic License Plate Recognition with Compression-Informed Transformers (IEEE ICIP 2022)
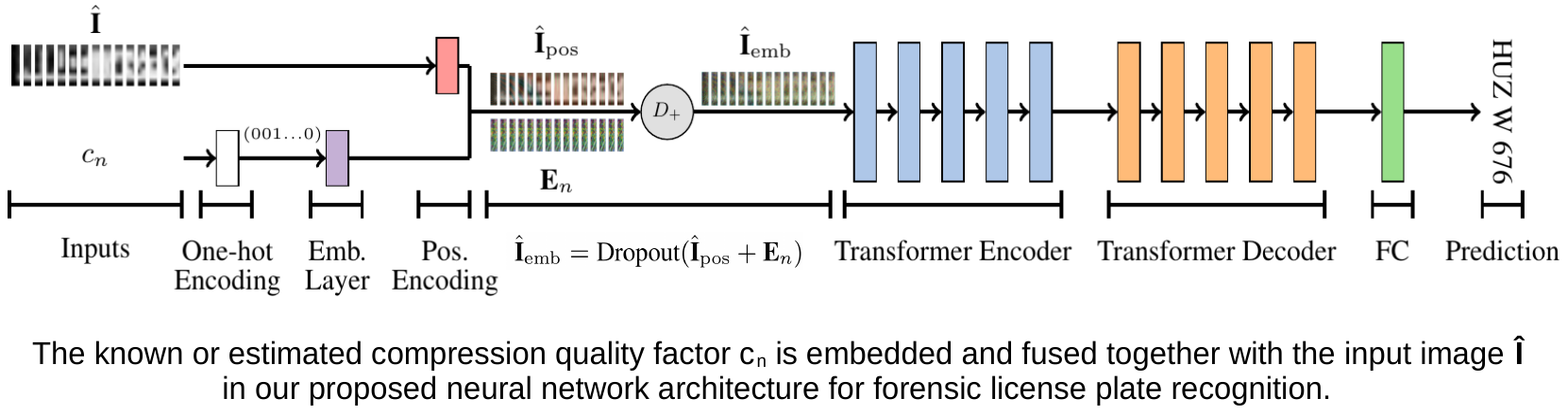
Forensic license plate recognition (FLPR) remains an open challenge in legal contexts such as criminal investigations, where unreadable license plates (LPs) need to be deciphered from highly compressed and/or low resolution footage, e.g., from surveillance cameras. In this work, we propose a side-informed Transformer architecture that embeds knowledge on the input compression level to improve recognition under strong compression. We show the effectiveness of Transformers for license plate recognition (LPR) on a low-quality real-world dataset. We also provide a synthetic dataset that includes strongly degraded, illegible LP images and analyze the impact of knowledge embedding on it. The network outperforms existing FLPR methods and standard state-of-the art image recognition models while requiring less parameters. For the severest degraded images, we can improve recognition by up to 8.9 percent points.
Towards Unconstrained Audio Splicing Detection and Localization with Neural Networks (MMFORWILD 2022, ICPR Workshop)
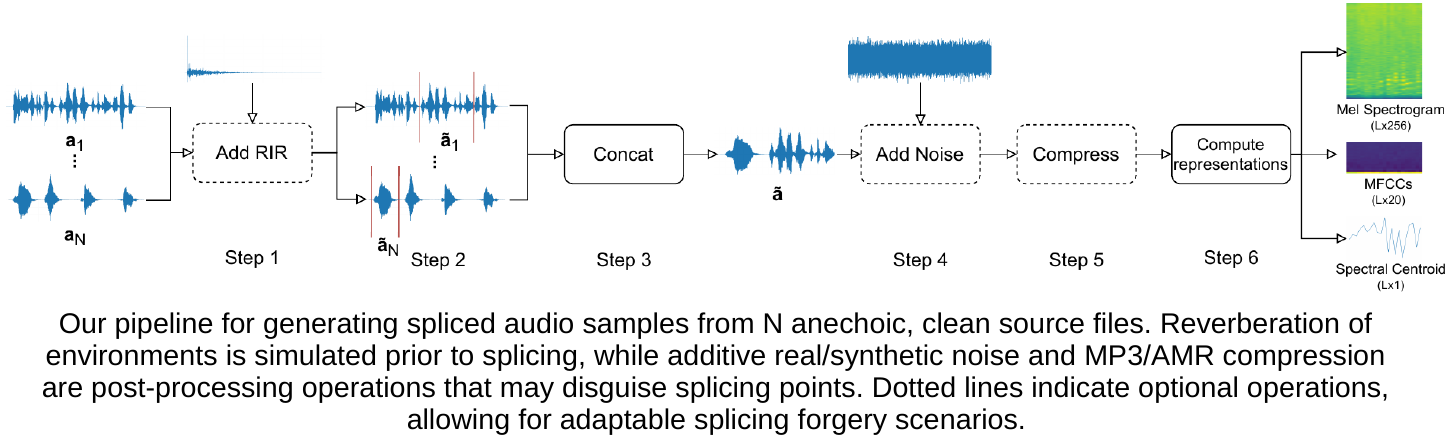
Freely available and easy-to-use audio editing tools make it straightforward to perform audio splicing. Convincing forgeries can be created by combining various speech samples from the same person. Detection of such splices is important both in the public sector when considering misinformation, and in a legal context to verify the integrity of evidence. Unfortunately, most existing detection algorithms for audio splicing use handcrafted features and make specific assumptions. However, criminal investigators are often faced with audio samples from unconstrained sources with unknown characteristics, which raises the need for more generally applicable methods.
With this work, we aim to take a first step towards unconstrained audio splicing detection to address this need. We simulate various attack scenarios in the form of post-processing operations that may disguise splicing. We propose a Transformer sequence-to-sequence (seq2seq) network for splicing detection and localization. Our extensive evaluation shows that the proposed method outperforms existing dedicated approaches for splicing detection as well as the general-purpose networks EfficientNet and RegNet.
Sequence-based Recognition of License Plates with Severe Out-of-Distribution Degradations (CAIP 2021)
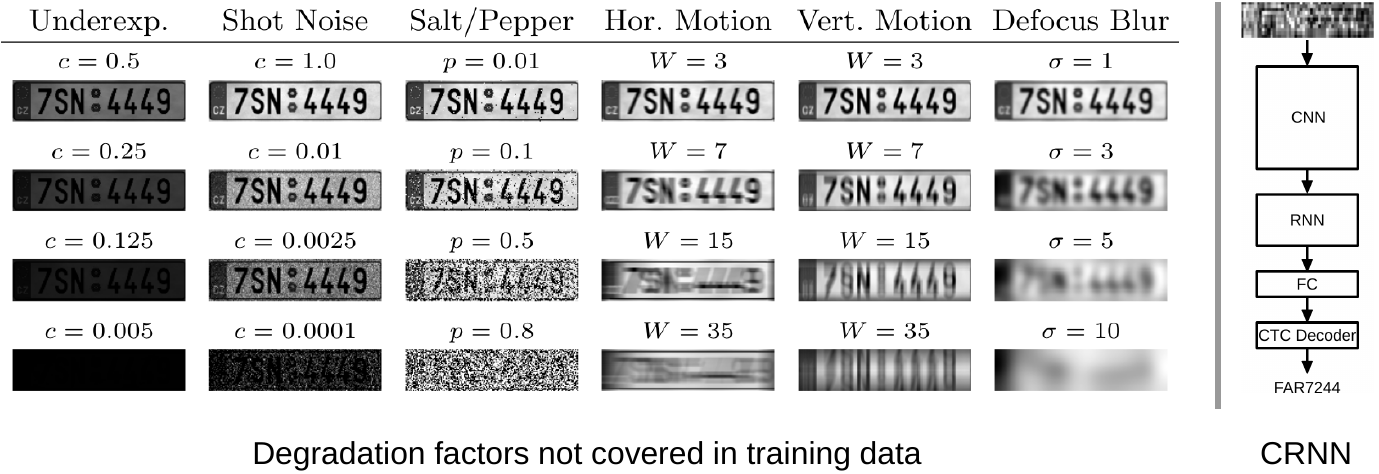
Criminal investigations regularly involve the deciphering of license plates (LPs) of vehicles. Unfortunately, the image or video source material typically stems from uncontrolled sources, and may be subject to severe degradations such as extremely low resolution, strong compression, low contrast or over- resp. underexposure. While LP recognition has a long history in computer vision research, the deciphering under such severe degradations is still an open issue. Moreover, since the data source is not controlled, it cannot be assumed that the exact form of degradation is covered in the training set. In this work, we propose using convolutional recurrent neural networks (CRNN) for the recognition of LPs from images with strong unseen degradations. The CRNN clearly outperforms an existing conventional CNN in this scenario. It also provides an additional particular advantage for criminal investigations, namely to create top-n sequence predictions. Even a low number of top-n candidates improves the recognition performance considerably.
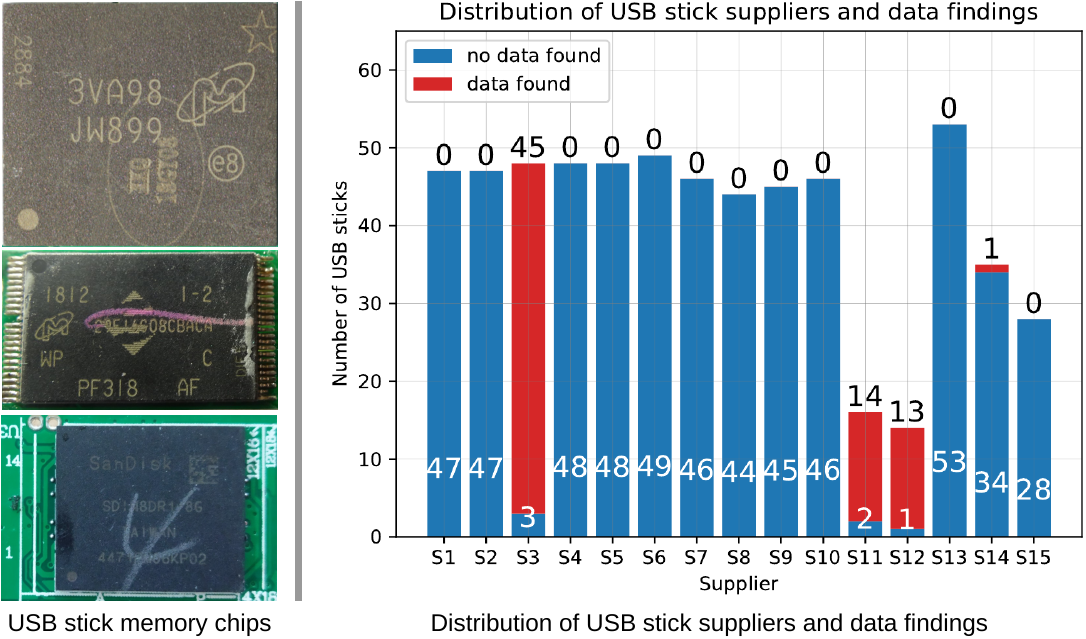
In Search of Lost Data: A Study of Flash Sanitization Practices (DFRWS EU 2021)
Best Paper Award
To avoid the disclosure of personal or corporate data, sanitization of storage devices is an important issue when such devices are to be reused. While poor sanitization practices have been reported for second-hand hard disk drives, it has been reported that data has been found on original storage devices based on flash technology. Based on insights into the second-hand chip market in China, we report on the results of the first large-scale study on the effects of chip reuse for USB flash drives. We provide clear evidence of poor sanitization practices in a non-negligible fraction of USB flash drives from the low-cost Chinese market that were sold as original. More specifically, we forensically analyzed 614 USB flash drives and were able to recover non-trivial user data on a total of 75 devices (more than 12 %). This non-negligible probability that any data (including incriminating files) already existed on the drive when it was bought has critical implications to forensic investigations. The absence of external factors which correlate with finding data on new USB flash drives complicates the matter further.
Analyse verbreiteter Anwendungen zum Lesen von elektronischen Büchern (Technical Report, 2019)
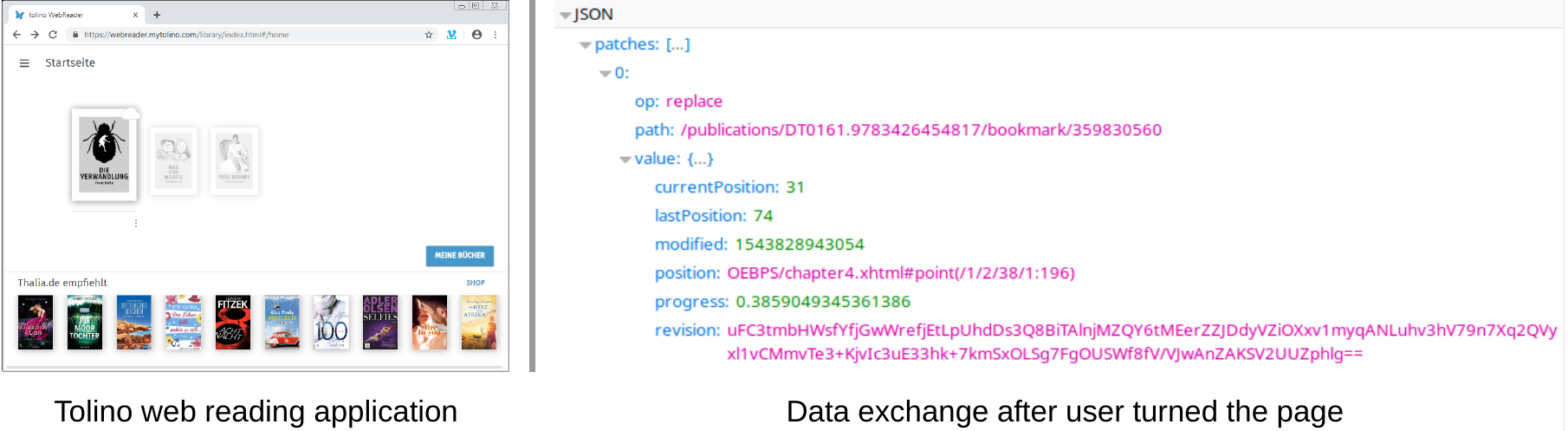
Der Marktanteil elektronischer Bucher (E-Books) am Buchmarkt wächst beständig. Um E-Books zu rezipieren, benötigt man spezielle Leseumgebungen, die als Software (im Browser oder als eigene Anwendung) oder als Spezialgerät (E-Reader) realisiert sein können. Diese Leseumgebungen sind geeignet, Daten über das Leseverhalten zu sammeln. Im Rahmen einer universitären Lehrveranstaltung wurden die Software-Leseumgebungen der beiden deutschen Marktführer Kindle und Tolino untersucht. Der vorliegende Bericht fasst die Ergebnisse dieser Analysen zusammen. Das Ergebnis ist eine umfassende Bestandsaufnahme der digitalen Spuren, die durch die Benutzung der Programme entstehen. Betrachtet wurden die zum Untersuchungszeitpunkt aktuellen Versionen der jeweiligen Webanwendungen und Android-Apps sowie des Kindle-Windows-Clients. Die Ergebnisse entstanden im Rahmen einer Übung zur Vorlesung “Fortgeschrittene forensische Informatik II” im Wintersemester 2018/19 an der Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg (FAU), die gemeinsam durchgeführt wurde vom Lehrstuhl fur Informatik 1 und dem Institut für Buchwissenschaft an der FAU.
PGP
| Key ID | 2498B03D7CA0C7DA |
| Fingerprint | 9F2D 4F5A 84BD 6135 7B5B 502D 2498 B03D 7CA0 C7DA |
| Public Key | Public Key |
Publications
2025
- Moussa, D., Hirsch, G., & Rieß, C. (2025). EnvId: A Metric Learning Approach for Forensic Few-Shot Identification of Unseen Environments. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 20, 2281-2296. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIFS.2025.3541534
URL: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2405.02119 - Schneider, J., Fukami, A., Lautner, I., Eichhorn, M., Moussa, D., Wolf, J.,... Westman, M. (2025). Poor Sanitization Practices and Questionable Digital Evidence: a Comprehensive Study of Scope and Impact of Recycled NAND Flash Chips. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing. https://doi.org/10.1109/TDSC.2025.3579237
2024
- Bergmann, S., Moussa, D., Brand, F., Kaup, A., & Rieß, C. (2024). Forensic analysis of AI-compression traces in spatial and frequency domain. Pattern Recognition Letters.
URL: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0167865524000503 - Moussa, D., Bergmann, S., & Rieß, C. (2024). Unmasking Neural Codecs: Forensic Identification of AI-compressed Speech. In ISCA (Eds.), Proc. Interspeech 2024 (pp. 2260-2264). Kos, GR.
URL: https://www.isca-archive.org/interspeech_2024/moussa24_interspeech.html# - Moussa, D., Huber, L., Hirsch, G., & Rieß, C. (2024). Now ForReal: Towards Practical Forensic Room Identification with Real-World Audio Data. In Proceedings - 16th IEEE International Workshop on Information Forensics and Security, WIFS 2024. Rome, IT: Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc..
URL: https://faui1-files.cs.fau.de/public/publications/mmsec/2024-Moussa-WIFS.pdf - Uhlenbrock, L., Cozzolino, D., Moussa, D., Verdoliva, L., & Riess, C. (2024). Did You Note My Palette? Unveiling Synthetic Images Through Color Statistics. In Association for Computing Machinery (Eds.), Proceedings of the 2024 ACM Workshop on Information Hiding and Multimedia Security (pp. 47-52). Baiona, ES: Association for Computing Machinery, Inc.
- Uhlenbrock, L., Moussa, D., Simmler, M., Canova, G., & Riess, C. (2024). Synthetische Bilddaten vor Gericht. Datenschutz und Datensicherheit.
2023
- Bergmann, S., Moussa, D., Brand, F., Kaup, A., & Rieß, C. (2023). Frequency-Domain Analysis of Traces for the Detection of AI-based Compression. In IEEE (Eds.), 2023 International Workshop on Biometrics and Forensics (IWBF). Barcelona, ES.
URL: https://faui1-files.cs.fau.de/public/publications/mmsec/2023-Bergmann-IWBF.pdf - Moussa, D., Hirsch, G., Wankerl, S., & Rieß, C. (2023). Point to the Hidden: Exposing Speech Audio Splicing via Signal Pointer Nets. In ISCA (Eds.), Proc. INTERSPEECH 2023 (pp. 5057 - 5061). Dublin, IE.
URL: https://faui1-files.cs.fau.de/public/publications/mmsec/2023-Moussa-Interspeech.pdf
2022
- Maier, A., Moussa, D., Spruck, A., Seiler, J., & Rieß, C. (2022). Reliability Scoring for the Recognition of Degraded License Plates. In Proceedings of the 2022 18th IEEE International Conference on Advanced Video and Signal Based Surveillance (AVSS). Madrid, ES.
URL: https://faui1-files.cs.fau.de/public/publications/mmsec/2022-Maier-AVSS.pdf - Moussa, D., Hirsch, G., & Rieß, C. (2022). Towards Unconstrained Audio Splicing Detection and Localization with Neural Networks. In Springer Cham (Eds.), Pattern Recognition, Computer Vision, and Image Processing. ICPR 2022 International Workshops and Challenges. (pp. 264-280). Montréal,Québec, CA: Springer.
URL: https://faui1-files.cs.fau.de/public/publications/mmsec/2022-Moussa-MMFORWILD.pdf - Moussa, D., Maier, A., Spruck, A., Seiler, J., & Rieß, C. (2022). Forensic License Plate Recognition with Compression-Informed Transformers. In IEEE (Eds.), 2022 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP) (pp. 406-410). Bordeaux, France, FR: IEEE.
URL: https://faui1-files.cs.fau.de/public/publications/mmsec/2022-Moussa-FLPR.pdf
2021
- Moussa, D., Maier, A., Schirrmacher, F., & Rieß, C. (2021). Sequence-based Recognition of License Plates with Severe Out-of-Distribution Degradations. In Springer, Cham (Eds.), Computer Analysis of Images and Patterns (pp. 175-185). Virtual Conference, CY: Springer Nature Switzerland AG.
URL: https://faui1-files.cs.fau.de/public/publications/mmsec/2021-Moussa-SRLP.pdf - Schneider, J., Lautner, I., Moussa, D., Wolf, J., Scheler, N., Freiling, F.,... Westman, M. (2021). In Search of Lost Data: A Study of Flash Sanitization Practices. In Proceedings of the Digital Forensics Research Conference Europe (DFRWS EU) 2021. Cyberspace.
URL: https://dfrws.org/presentation/in-search-of-lost-data-a-study-of-flash-sanitization-practices/
2019
- Benenson, Z., Berger, F., Cherepantsev, A., Datsevich, S., Do, L., Eckert, M.,... Zlatanovic, J. (2019). Analyse verbreiteter Anwendungen zum Lesen von elektronischen Büchern.
URL: http://nbn-resolving.de/urn:nbn:de:bvb:29-opus4-125519


